Why is physical activity important?
Physical activity stimulates the concentration!
Persistent physical activity results in a better circulation and therefore to an increased supply of oxygen to the brain1,2. Brain functions are improved2. Solving tasks and steering selective attention is easier1. Children exercising regularly are more concentrated, focused and calm1. They show probably better academic performances2,3.
1 Bidzan-Bluma, I., Lipowska, M. (2018). Physical Activity and Cognitive Functioning of Children: A Systematic Review.
2 Sember, V., et al. (2020). Children’s Physical Acticity, Academic Performance, and Cognitive Functioning: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
3 Poitras, V. J., et al. (2016). Systematic review of the relationships between objectively measured physical activity and health indicators in school-aged children and youth.

Physical activity is, makes and keeps you heatlthy!
Physical activity is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle, due to its beneficial effects on skeletal, metabolic and cardiovascular functions of the human body1. Regular physical activity build muscle mass, improves endurance and increases the bone density2,3. The risk of many diseases, including obesity, cardiorespiratory or mental diseases, decreases3,4,5. Physical activity is healthy and preventive for physical and mental health2,3,4.
1 Sember, V., et al. (2020). Children’s Physical Acticity, Academic Performance, and Cognitive Functioning: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.
2 Bidzan-Bluma, I., Lipowska, M. (2018). Physical Activity and Cognitive Functioning of Children: A Systematic Review.
3 Poitras, V. J., et al. (2016). Systematic review of the relationships between objectively measured physical activity and health indicators in school-aged children and youth.
4 Gomes, T. N., et al. (2020). A Systematic Review of Children’s Physical Activity Patterns: Concept, Operational Definitions, Instruments, Statistical Analyses, and Health Implications.
5 Jones, D., et al. (2020). Association between fundamental motor skills and physical activity in the early years: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
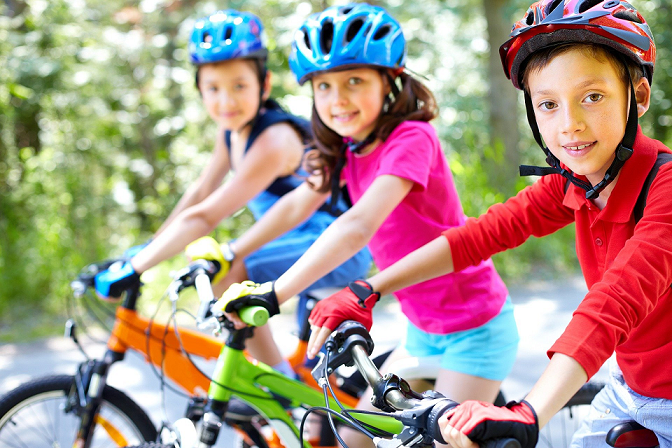

Physical activity is fun!
On the one hand, physical activity stimulates the production of happiness hormones, e.g. dopamine and serotonin. An incline of these hormones creates emotional rewards, meaning we feel happy and joyful1. On the other hand, one achieves personal progress and has a sense of achievement by movement and sports, resulting in positive effects on self-confidence2,3. Own competencies can be recognized and expanded, motivation and the fun of exercising increase2,3.
1 Di Liegro, et al. (2019). Physical Activity and Brain Health.
2 Klos, L., et al. (2020). Interventions to Promote Positive Affect and Physical Activity in Children, Adolescents and Young Adults – A Systematic Review.
3 Tendinha, R., et al. (2021). Impact of Sports Education Model in Physical Education on Students’ Motivation: A Systematic Review.
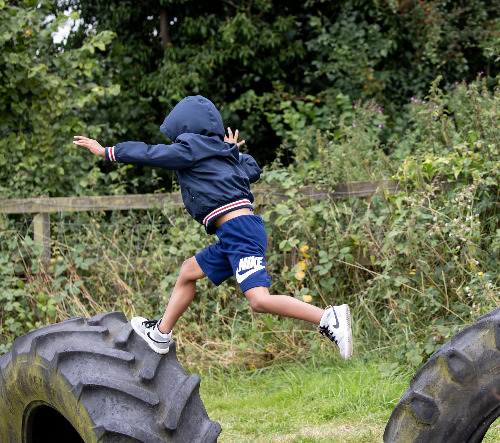

Physical activity promotes motor skills!
Physical activity is closely related to basic motor skills and increases them significantly1,2,3. Motor skills are important for the coordination and mobility2. Regular physical activity specifically promotes these skills1,2. Physical activity plays a major role especially in childhood, because motor skills are developed at an early age1,2. Musculoskeletal, cardiorespiratory, sensory and neurological functions are combined by movement through learning processes2. Learning and maintenance of motor skills have present and future benefits2.
1 Jones, D., et al. (2020). Association between fundamental motor skills and physical activity in the early years: A systematic review and meta-analysis.
2 Lopes, L., et al. (2020). A Narrative Review of Motor Competence in Children and Adolescents: What We Know and What We Need to Find Out.
3 McDonough, D. J., et al. (2020). Effects of Physical Activity on Children’s Motor Skill Development: A Systematic Review of Randomized Controlled Trials.

Physical activity does so much more!
In addition to the physiological and psychological areas, that are positively influenced by physical activity, there are many other levels in which exercise has a positive effect, e.g. in social development of children or under ecological aspects. These lists can be continued almost infinitely.
We would like to challenge and invite you, to try it out yourself and integrate more movement in your everyday life (again). We are looking forward to your criticism and feedback: actipros@leibniz-bips.de.

 Deutsch
Deutsch  Englisch
Englisch